Assembly BOMs vs. Production BOMs: Understanding the Differences and When to Use Each
In Business Central, selecting the right type of Bill of Materials (BOM) is an important decision to support efficient manufacturing operations. Whether to use Assembly BOMs or Production BOMs depends on the complexity of your products, the level of process tracking required, and your business's operational needs. So, which should you use? It depends on your situation.
Assembly BOMs
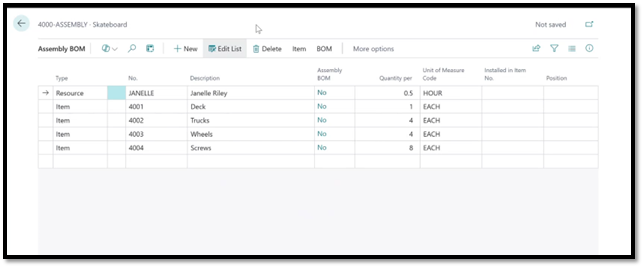
Assembly BOMs are the master data of components that go into a finished product. An Assembly BOM is used for simple assembly scenarios involving components with minimal resource utilization.
Creating kits is an example of what would be a good use of an assembly BOM. This type of BOM is used when you are combining pre-existing components into a single product without the need for complex manufacturing processes. An example is assembling a First Aid Kit, where you add items such as band-aids, alcohol wipes, scissors, and other items commonly found in a typical first aid kit. All the items you are adding to this kit are already assembled. All that is required is that you collect them and put them in the same pack. An installation Hardware kit is another example, this contains a hammer, screwdriver, power drill, and other items that only need to be collected and packed together to assemble.
Assembly BOMs are straightforward to set up and manage. You can add labor as a resource to account for estimated costs, but there is no way to track actual labor time. This simplicity makes it ideal for businesses that do not need detailed production tracking.
Also, Assembly BOMs are available under the Essentials license in Business Central, which can result in cost savings compared to the Premium license required for Production BOMs.
Assembly BOM for a skateboard.
Production BOMs
Production BOMs, on the other hand, are utilized for more complex manufacturing processes or where detailed operations and costs need to be tracked. Production BOMs and Routings enable businesses to accurately track labor and material costs, manage production schedules, and efficiently handle subcontracting activities.
An example of an activity for a Production BOM might be manufacturing a pen from raw materials. We would need to track each step, such as molding the housing, assembling the ink cartridge, machining the barrel, and attaching the clip. This kind of detailed tracking is not possible in an Assembly BOM; it requires a Routing and a Production BOM
Production BOMs allow you to create planned Scrap percentages for components, and - when using Routing Links – you can assign materials to be used at specific operations in the Routing, which can be useful when needing to time the consumption of inventory closely to the point of use.
Production BOMs would also be the best option if you need to maintain multiple versions of the BOM, either as an audit trail or perhaps to reuse it at some point in the future. Assembly BOMs do not allow you to maintain previous versions.
Production BOMs/Routings are most effective when you need to monitor production at an operational level, especially if you are working with multiple levels of subassemblies or require external services. Production BOMs provide the structure and flexibility needed to manage these complex products.
The Manufacturing module of BC, including Production BOMs and Routings, does require a Premium license, so if your production does not require this level of complexity, you can save some money by utilizing Assembly BOMs instead.
Project Planning Lines
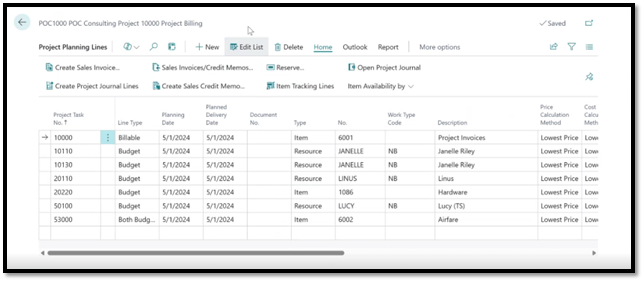
A similar function to BOM’s is Project Planning Lines, which can be used within the Projects module of Business Central to store a list of components, particularly useful in engineer-to-order environments where each product is custom-designed based on specific customer requirements and every order must undergo an engineering phase before production can begin.
An example of this is a company that builds custom electronic control panels, where each unit may have different wiring, configurations, and materials depending on the client’s specific needs. Or, perhaps an Engineering group wants to make prototypes before actual production. The Project Planning Lines can be used to make a list of the materials they use, and they can just build it and consume the inventory.
The Projects module enables businesses to track all associated costs, from engineering and design to production, within a single project. While Project Planning Lines are not typically used for standard manufacturing, they are useful for managing unique, one-off builds that require detailed cost tracking and planning.
An example of a project planning line.
Ultimately, the choice between Assembly or Production BOMs should be guided by the complexity of your products, the detail required for tracking production activities, and your licensing considerations. When working with more warehousing or the assembly of items, such as kitting, Assembly is the best choice.
On the other hand, if you’re manufacturing more complex products, then Production would be necessary to support your operations. By selecting the right BOM type, you can streamline your operations, improve cost control, and ensure that your manufacturing processes align with your business goals.
Assembly or Production BOMs comparison chart.